

GAPK is an alternative Genetic Algorithm based do novo motif discovery application. GAPK consists of three main components: 1) Data Pre-processing to filter out noisy data in terms of search space reduction; 2) A Novel GA framework that targets to discover candidate motif models; 3) Post-processing for optimizing the predicted motif models from 2). Experimental verified binding sites associated with certain transcription factors from public domains are employed as prior-knowledge, especially designed for filtering noisy data and initializing the population. A mismatch-based metric is proposed as fitness function to guide the evolutionary process in 2). New genetic operations work together to potentially increase the probability of clustering similar k-mers to form better candidate motif models. A three-steps motif model refinement process aims to minimize the number of false positive instances and at the same time to maximize the number of true binding sites in the candidate models. In the detailed comparative studies, GAPK demonstrates the robustness and outperforms some well-known tools such as MEME, AlignACE, as well as two other GA approaches GAME and GALF-P.
For technical assistance or bugs please email to: A/Professor Dianhui Wang
The program can be downloaded from the following link.
| Executable files | Windows platform Download here. |
|---|---|
| Linux platform Download here. |
The source codes of GAPK were implemented using C/C++ and developed using Red Hat. Although the codes has been compiled and tested successfully on both windows platform (gcc version 3.4.5 under Windows XP sp2) and linux platform (gcc version 4.1.2 under Red Hat Linux version 2.6.18-92.e15), the authors cannot guarantee that it would not come across any compatible problems on other platforms. We appreciate feedbacks regarding to any implementation issues.
To run GAPK,
1) choose the right distribution and extract the zip file.
2) For windows users: simply run the executable file "GAPK_2010.exe" on the command prompt.
For linux users: in the GAPK directory, run from the terminal by typing "GAPK_2010".
The command line is: GAPK_2010 -i <seq_file> -freq <freq_file> optional arguments]
| Parameter | Required (Y/N) | Description |
| -h | N | shows the help menu. |
| -i <seq_file> | Y | seq_file is the name of the input sequences file that contains DNA sequences.
(Note: the input file must be in fasta format and only contain A,C,G and T in the sequence.) |
| -freq <freq_file> | Y | freq_file is the name of the file that contains 3rd order Markov background frequency information. |
| -pk <pk_file> | N | The file contains prior-knowledge (true binding sites) one site per line. An example of the pk_file: TATAAA TATCAA TATTAA TTTAAA |
| -o <output_file> | N | The output file (Default: gapk.out). |
| -k <kmer> | N | The expected motif width (Default=8). |
| -ns <numperseq> | N | The maximum number of binding sites in one motif model per sequence (Default=2). |
| -d <T/F> | N | The flag of performing the motif discovery on both forward and reverse strands (True) or not (False) (Default=T). |
| -g <generation> | N | The maximum number of generations in genetic algorithm search (Default=1000). |
| -p <population> | N | The population size in genetic algorithm search (Default=600). |
| -r <replacement_rate> | N | The replacement rate, a novel genetic operator introduced by GAPK to avoid the algorithm trapped into a local optimizing solution in the genetic algorithm search (Default=0.8). |
| -w <winner_rate> | N | A hybrid approach for reforming the population after every generation by applying both winners-take-all selection and tournament selection. If the winner-table-all rate in genetic algorithm search is 0.2, so the tournament selection rate is 0.8. (Default=0.25) |
| -lc <complexity_value> | N | The minimum complexity rate of a motif. Valid values are [0, 10]. (Default=0.01) |
| -f <T/F> | N | The filtering method (Default=T) is introduced in GAPK for noise data reduction. If it is set as 'True', the user must provide the prior-knowledge file. |
| -pkper <pk_percent> | N | The percentage of Prior-knowledge is used for initializing the population in genetic algorithm search (Default=0.8). |
| -perpk <pk_amount> | N | The amount of Pre-knowledge is randomly selected from the pre-knowledge file, which is used for noise reduction and population initialization. Valid values are (0,1]. (Default=1) |
| -delta <delta> | N | Any two motif models with a small amount of IC difference (Default=0.05) will be merged in the post-processing stage. Valid values are (0,1). |
| -post <T/F> | N | The post-processing flag (Default=T). If it is set as True, the three steps final model refinement process is switched on. |
The command line to use the perl script is,
perl BackExtract.pl -seq fastafile -x len [-out outfilename]
fastafile is the fasta file name that stores the background sequences.
len is the markov order (default is 3). In GAPK, the 3rd order markov chain model is used.
outfilename is the output file name, which is the compulsory file <freq_file> required by GAPK.
The <seq_file> of fasta format that contains DNA sequences and <freq_file> which contains the background frequencies of oligonucleotides are the only two compulsory parameters for GAPK. GAPK will fail to run by given a file with wrong format or empty file. In the <seq_file>, the sequences are believed to be pure DNA sequences and co-regulated by the same protein. The co-regulation can be established through gene expression analysis or other in vivo method such as CHIP-Seq, CHIP-PET, etc. These methods have been widely use for genome wide motif discovery. The <freq_file> is generated by using the Markov Chain model .
Step 2:
If users aim to use the prior-knowledge option for filtering noise data, a text file that contains true binding sites need to be prepared. The binding sites are only composed of A,C,G and T. Consensus patterns that have IUPAC letters are not supported in this version. The format of prior-knowledge <pk_file> file is given in the Usages section. If the prior-knowledge is provided, the length of kmer is automatically set as the same length as the length of the true binding sites stored in prior-knowledge.
Step 3:
Specify any other parameters, such as width of the kmer as 10 (-k 10), number of sites per sequence as 3 (-ns 3), number of generations as 500 (-g 500), replacement probability as 0.3 (-r 0.3), and percentage of prior-knowledge is used for initializing the population as 0.4 (-pkper 0.4).
(Note: If the top model is kept after 100 generation, the genetic algorithm search of GAPK is finished. )
For example, the command line to discover motifs from upstream DNA sequences for genes believed to be co-regulated by MEF2 is,
GAPK_2010 -i MEF2.fa -freq MEF2.back -pk MEF2.sites -g 1000 -p 500 -r 0.7 -perpk 0.8 -pkper 0.7 -o MEF2.output
Step 4:
The output file MEF2.output contains the final output motifs returned by GAPK. The following is the output result.
GAPK: Motif Discovery Using Genetic Algorithm Incorporating Prior Knowledge
by Dianhui Wang and Xi Li, 2009.
The Final Results:
Motif Rank #1
Motif Model Mismatch Score: 0.389717 Information Content: 8.31977
Complexity: 0.0850676 Consensus: CTATATTTAG
No. of sites: 17
Position Frequency Matrix
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
A 0 0 17 5 11 3 7 1 14 3
C 15 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
G 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 9
T 2 17 0 12 6 14 10 15 0 4
|
- Motif Relative Model Mismatch
Score (RMMS) is used as a metrics that quantifies the evolutionary constraint on the motif models. A motif model with a small RMMS stands a high degree of
conservation associated with the model rareness. The RMMS formula is given by:
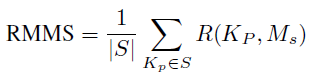
(S is the motif model that consists of a collection of binding sites with a fix length of k. |S| represents the cardinality of the set S. M is the motif Position Frequency Matrix (PFM) model. Kp represents a single k-mer in the set S. R() denotes the relative mismatch score RMS of a k-mer )
- Complexity
is the motif complexity value, proposed by Mahoney et.al [1]. It can effectively measure the model compositional structure
to exclude the models with low complexity scores. An individual with a complexity score less than a threshold value will be removed from the
population. The formula is given by:
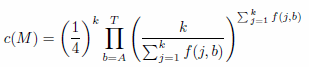
- Information content is given by:
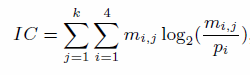
(k is the length of binding site. m(i,j) is the frequency of DNA base i in position j, pi is the background frequency of DNA base i.)
- Each line in the list of predicted sites is arranged in the following order. a) Sequence name, b) Actual site (forward/reverse complement), c) strand of the site, 1(forward), 0(reverse complement); d) the start and end position where the site appear in the input strand given; e) individual site mismatch score against the Motif Model.
|
|
|
|