MISCLUSTER is a divisive hierarchical clustering method for do nova motif discovery. MISCLUSTER employ mismatch value for cluster initialization. The initialization method reduce the sequence search space and thus allows effective time reduction. Unlike most standard hierarchical clustering algorithm, our hierarchical clustering framework is tailored to suit motif discovery in considerations on the clusterability of the Kmers and also the effect of the background sequences. MISCLUSTER method work under the observation there is an upper bound on mismatch between the true binding sites of a protein. The pre-selected initial clusters are further branches using binary divisive algorithm to improve the specificity and sensitivity. Heuristic rules are introduced for sub-cluster selection and as branching stopping criterion.
For technical assistance or bugs please email to: A/Prof Dianhui Wang
The program can be downloaded from the following link.
| Executable file | Windows platform Download here. |
| Markov chain model generator (perl script) | Any platform. Download here. |
MISCLUSTER is implemented using C/C++ and developed using Dev-C++ version 4.9.9.2 which is available at http://bloodshed.net. The program has also been compiled sucessfully in Microsoft Visual Studio 7.0.
To run the program, simply extract the executable file (e.g. .exe) and it can be run on the command prompt. The usages of Markov chain perl script can be found in section below.
miscluster [parameters]
| Parameter | Required | Description |
| -h | N | shows the help menu. |
| -f [filename] | Y | filename is the input sequences file name in fasta format. |
| -l x | Y | Specify the expected motif length x. Valid values are [6, 20]. |
| -m y | Y | Specify the maximum mismatch between the kmers. Integer value between (0, l/2) |
| -b [filename] | Y | Where filename is the file name that store the 7th order markov chain generated using perl script. We have prepared the background file for several species (see the next sub-section). |
| -z [filename] | Y | The 7th order foreground markov chain generated using perl tool. |
| -k [opt] | N | Specify the cluster initialization method. Value options are: 1-using core motif, 2-using enumeration. |
| -r | N | If specify, only the given input sequences strand will be used in motif discovery. |
| -o [filename] | Y | Output file name that stores the discovered motif. |
| -thr [value] | N | Specify the post-scanning threshold (0, 1]. Default value is 0.75. This threshold value is very important as it determines the final motifs set returned after the candidate motifs have been selected at the end of hierarchical branching. The guideline for this parameter is discussed in the paper. |
| -s | N | The default scoring function to select core motif is based on MAP score. Once this switch is specified, the Kmer surprise score will be used instead. |
| -v [value] | N | Specify the number of initial clusters [10,100]. The default is 40. |
| -t [value] | N | Specify the number of top ranked motifs to return. The default is 10. |
| -j | N | If specified, the initial sequences will be selected based on markov chain model. |
| -i [value] | N | Number of initial sequences use to generate the core motifs. Warming!!! the computational time would be great if too many initial sequences are used. |
| -c [value] | N | Minimum complexity value of a motif. Valid values are [0, 10]. The default value is 0.15. |
The command line to use the perl script is,
perl BackExtract_modi.pl -seq fastafile -x len [-out outfilename]
fastafile is the fasta file name that stores the background sequences.
len is the markov order (default is 3). In MISCLUSTER, the seventh order markov chain model is used.
outfilename is the output file name.
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae/Yeast | Download |
| Human | Download |
| Mouse | Download |
| Escherichia coli | Download |
MISCLUSTER require users to prepare input sequences that believe to be co-regulated by the same protein. The co-regulation can be established through gene expression analysis or other in vivo method such as CHIPchip, CHIP-PET, etc (ref). These methods have been widely use for genomewide motif discovery.
Step 2:
Users have to prepare the background and input sequences markov model using the perl script. The markov model is based on 7th order markov model which can be generated using the Perl script provided above.
Step 3:
Decides the motif length (-l) and mismatch value (-m). For example, the command line to discover motifs from upstream DNA sequences for genes believed to be co-regulated by GAL4 protein is,
miscluster -f GAL4_YPD.fsa -l 17 -m 7 -k 2 -o gal4.output -thr 0.75 -b yeast_7c.back -z gal4.fore
The mismatch value is usually set between (0, l//2]. One should attempt with smaller mismatch value initially before proceeding to larger values.
Step 4:
The output file gal4.output contains the top 10 motifs returned by MISCLUSTER. The following is the top 1 motif.
Motif rank #1 Position Count Matrix >iYGR295C-1 AGGGCTCCTCTACTTCG 1 852 0.8690 |
Descriptions:
|
|
|
|
2.van Helden, J. Regulatory sequence analysis tools Nucl. Acids Res., 2003, 31, 3593 - 3596
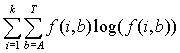 .
.